Introduction of 342 BNS
Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS) Section 342 criminalizes the counterfeiting of devices or marks used to authenticate documents or electronic records. This provision ensures that forged documents cannot be disguised as genuine through fake seals, stamps, or digital signatures. It applies both to high-value documents under Section 338—such as wills, securities, and contracts—and to other records, including digital ones. By prescribing punishments ranging from life imprisonment to seven years with a fine, this section upholds trust in India’s legal, financial, and digital systems. Replacing IPC Sections 475 and 476, Section 342 strengthens protections for modern documentation.
The Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS) Section 342 replaces the old Indian Penal Code (IPC) Section 475,476.
What is BNS Section 342 ?
BNS Section 342 criminalizes the act of counterfeiting devices or marks used for authenticating documents or electronic records. This includes creating fake marks to give forged documents the appearance of authenticity or possessing counterfeit materials with intent to use them. The section applies to documents described in Section 338 and other types of documents. Punishments vary depending on the type of forgery, emphasizing safeguarding the integrity of legal and official documentation.

Under Section 342 of the bns act 2023
“Whoever counterfeits, or possesses any device or mark used for authenticating documents or electronic records, intending that it shall be used for forgery—
(1) If the document is described under Section 338 → punishment may extend to life imprisonment or 7 years with fine.
(2) If the document is any other document or electronic record → punishment may extend to 7 years with fine.”
(This provision replaces IPC Sections 475 & 476.)
1. Meaning of Section 342
This section punishes the act of:
- Counterfeiting marks/devices → e.g., official stamps, seals, or digital signatures.
- Possession of counterfeit authentication materials → keeping fake seals with the intent to use them.
- Forgery intent → making a forged document look genuine.
Example → Using a fake digital signature to validate a forged property contract.
2. Who is Covered?
- Individuals → A person creating or keeping counterfeit stamps/seals.
- Hackers or digital offenders → Forging digital signatures or electronic authentication marks.
- Organizations or groups → Possessing counterfeit authentication devices for fraud.
3. Punishments under Section 342
- For documents under Section 338 (high-value documents like wills, securities, contracts):
- Life imprisonment or up to 7 years + fine.
- For other documents (including electronic records):
- Imprisonment up to 7 years + fine.
Example → A forged government bond with a fake seal may attract life imprisonment.
4. Nature of the Offence
- Subsection (1):
- Non-cognizable → Police need Magistrate’s permission to investigate.
- Bailable → Accused can apply for bail.
- Non-compoundable → Cannot be settled privately.
- Subsection (2):
- Non-cognizable → Requires Magistrate’s approval.
- Non-bailable → Bail not a matter of right.
- Non-compoundable.
- Trial By → Magistrate of the First Class.
5. Essential Ingredients
For conviction under BNS 342, prosecution must prove:
- The device or mark is counterfeit.
- The accused made, possessed, or used it.
- The accused intended it to be used for forgery.
- The document falls under either Section 338 or other documents/e-records.
6. Examples of BNS Section 342
- Example 1 – Forging a Seal on a Security (Section 338)
A man makes a fake government seal to authenticate a forged security bond. → Punishable with life imprisonment or up to 7 years. - Example 2 – Fake Digital Signature (Other documents)
A hacker creates a forged digital signature for a property sale agreement. → Punishable with up to 7 years + fine. - Example 3 – Possession without Use
A person keeps fake university authentication stamps intending to issue fake certificates. → Punishable even without actual use.
7. Importance of BNS Section 342
- Protects authenticity of seals and digital marks.
- Ensures public trust in both physical and electronic documents.
- Punishes not only forgery but also preparatory acts (making or possessing counterfeit materials).
- Adapts law to digital age by covering electronic records and e-signatures.
Section 342 BNS Overview
BNS Section 342 addresses the offense of counterfeiting devices or marks used for authenticating documents. It criminalizes the act of forging or counterfeiting marks to give forged documents the appearance of being authentic. This applies to documents described under Section 338 or any other document, including electronic records. Possessing counterfeit materials with the intent to use them for fraudulent purposes is also punishable under this section.
Key Points of BNS Section 342
- Forgery of Authentication Devices for Section 338 Documents
Under subsection (1), counterfeiting marks or devices used for authenticating documents listed in Section 338, such as wills or valuable securities, is an offense. The intent is crucial, as the law targets those who create or possess such counterfeit materials intending to use them for forgery. This helps protect public trust in critical legal and financial documents. - Forgery for Non-Section 338 Documents or Electronic Records
Subsection (2) extends the law to other documents, including electronic records. Counterfeiting authentication marks for documents outside Section 338 is punishable. This ensures that all forms of documents, traditional or digital, are safeguarded from forgery. - Possession of Counterfeit Materials
Mere possession of materials bearing counterfeit authentication marks with intent to use them for forgery is a crime. It prevents potential misuse before any forgery occurs, emphasizing intent over actual execution of fraud. - Punishments under Subsection (1)
For counterfeiting authentication marks on Section 338 documents, the punishment includes life imprisonment or up to seven years, along with a fine. This reflects the seriousness of tampering with high-value or critical documents. - Punishments under Subsection (2)
For counterfeiting marks for other documents or electronic records, the punishment is imprisonment for up to seven years and a fine. It emphasizes the growing importance of protecting digital records. - Classification of Offenses
Subsection (1) is non-cognizable, bailable, and non-compoundable. Subsection (2) is non-cognizable, non-bailable, and non-compoundable. This distinction is based on the severity and scope of forgery. - Intent as a Key Factor
The section focuses on intent rather than just possession or usage. If a person possesses counterfeit materials with the purpose of forgery, they can be punished, even if the forgery hasn’t been carried out. - Trial Jurisdiction
Both offenses under subsections (1) and (2) are triable by a Magistrate of the first class. This ensures a fair trial for individuals accused of counterfeiting marks or possessing counterfeit materials. - Safeguarding Digital Records
Subsection (2) highlights the importance of protecting electronic records, aligning with modern needs as digital transactions and records become increasingly common. - Public Trust in Legal Processes
By criminalizing counterfeiting marks used for authenticating documents, this section ensures that citizens trust legal and financial systems. It acts as a deterrent against fraudulent activities targeting essential documents.
Examples of BNS Section 342
Example 1: Counterfeiting a Seal for a Valuable Security Document
A person creates a counterfeit seal resembling the official stamp used to authenticate a government bond (a valuable security under Section 338). They then attach the counterfeit seal to forged bonds and attempt to sell them. This act falls under BNS Section 342(1) as it involves counterfeiting marks used for authenticating Section 338 documents. The offender may face imprisonment for life or up to seven years, along with a fine.
Example 2: Forging a Mark for an Electronic Document
A hacker designs a fake digital signature resembling the one used by a public authority to authenticate official electronic records. They use this fake signature to validate forged property sale agreements sent via email. This act comes under BNS Section 342(2), which addresses counterfeiting marks for electronic records. The hacker could be sentenced to up to seven years in prison and fined for their actions.
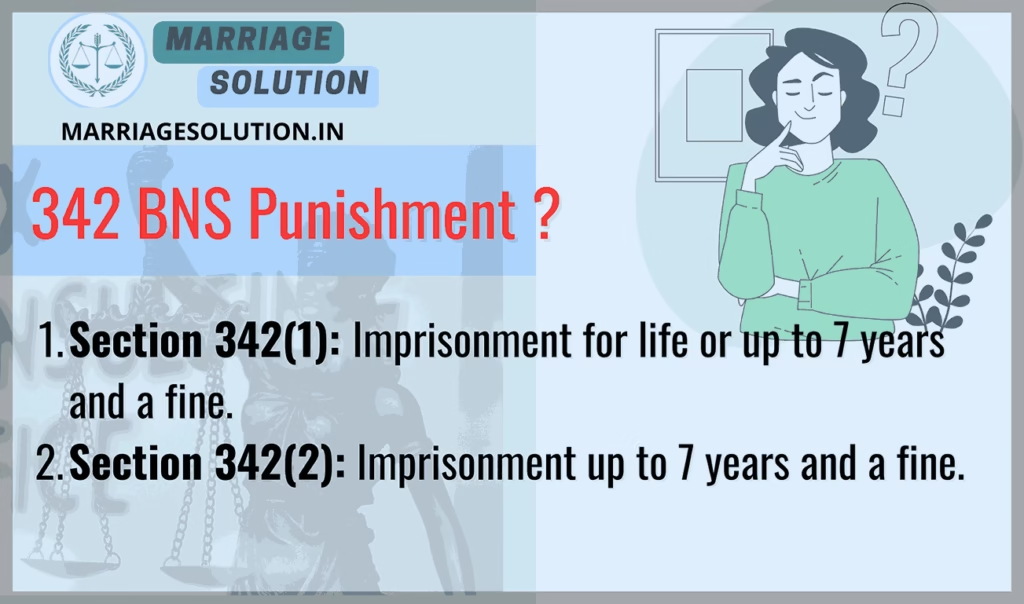
BNS 342 Punishment
- Section 342(1): Imprisonment for life or up to 7 years and a fine.
- Section 342(2): Imprisonment up to 7 years and a fine.
BNS 342 bailable or not ?
Subsection (342)(1): Bailable – Forgery involving Section 338 documents is bailable.
Subsection (342)(2): Non-Bailable – Forgery of other documents or electronic records is non-bailable.
Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita Section 342
| BNS Section | Offense | Punishment | Bailable / Non-Bailable | Cognizable / Non-Cognizable | Trial By |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 342(1) | Counterfeiting marks or devices for documents under Section 338 (wills, securities, contracts). | Life imprisonment or up to 7 years + fine. | Bailable | Non-cognizable | Magistrate of the First Class |
| 342(2) | Counterfeiting marks or devices for other documents or electronic records. | Imprisonment up to 7 years + fine. | Non-bailable | Non-cognizable | Magistrate of the First Class |
Comparison: BNS Section 342 vs IPC Sections 475 & 476
| Section | Offense | Punishment | Bailable / Non-Bailable | Cognizable / Non-Cognizable | Trial By |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BNS Section 342(1) | Counterfeiting authentication marks/devices for documents under Section 338 (wills, securities, contracts). | Life imprisonment or up to 7 years + fine. | Bailable | Non-cognizable | Magistrate of the First Class |
| BNS Section 342(2) | Counterfeiting authentication marks/devices for other documents or electronic records. | Imprisonment up to 7 years + fine. | Non-bailable | Non-cognizable | Magistrate of the First Class |
| IPC Section 475 (Old) | Counterfeiting device or mark used for authenticating documents like valuable securities or wills. | Life imprisonment or up to 7 years + fine. | Bailable | Non-cognizable | Magistrate of the First Class |
| IPC Section 476 (Old) | Counterfeiting device or mark for any other documents. | Imprisonment up to 7 years + fine. | Non-bailable | Non-cognizable | Magistrate of the First Class |
BNS Section 342 FAQs
What is the purpose of BNS Section 342?
BNS Section 342 aims to penalize counterfeiting marks or devices used for authenticating documents and possessing such counterfeit materials.
What are the punishments under BNS Section 342?
For Section 342(1), the punishment is life imprisonment or up to 7 years and a fine. For Section 342(2), the punishment is up to 7 years and a fine.
Is BNS 342(1) bailable?
Yes, offenses under Section 342(1) are bailable.
Can someone be punished for merely possessing counterfeit materials?
Yes, possession with intent to use counterfeit materials is punishable under BNS Section 342.
What kind of documents does BNS Section 342 cover?
Section 342(1) covers documents described in Section 338, while Section 342(2) includes other documents and electronic records.
Who tries cases under BNS Section 342?
Cases under both subsections are tried by a Magistrate of the first class.
Conclusion
BNS Section 342 plays a vital role in protecting the authenticity of documents and digital records. By punishing not only the act of forgery but also the creation or possession of counterfeit authentication devices, it ensures that fraudsters cannot deceive people or institutions by making false documents appear genuine. With separate punishments for Section 338 documents and other records, the law balances severity with fairness. Its recognition of digital forgery also reflects the changing times, ensuring safeguards in both physical and electronic domains. Overall, Section 342 is a powerful deterrent against counterfeiting that maintains public trust in official, financial, and legal documentation.
Need Legal Support?
If you are dealing with court cases, marriage problems, or any other legal issue, our team at Marriage Solution – Lawyer Help is here for you. Simply fill out our quick online enquiry form, and we’ll connect you with the right legal expert to support your needs.
Finished with BNS 342 ? Continue exploring the next provisions of the Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS), 2023. Each section includes explanations, examples, and plain-language breakdowns for easy understanding.
- 343 BNS : Fraudulent cancellation, destruction, etc., of will, authority to adopt, or valuable security .
- https://marriagesolution.in/bns_section/343-bns/
- 344 BNS : Falsification of accounts .
- https://marriagesolution.in/bns_section/344-bns/
- 345 BNS : Property mark .
- https://marriagesolution.in/bns_section/345-bns/
- 346 BNS : Tampering with property mark with intent to cause injury .
- https://marriagesolution.in/bns_section/346-bns/
- 347 BNS : Counterfeiting a property mark.
- https://marriagesolution.in/bns_section/347-bns/
Full IPC Section List: https://marriagesolution.in/ipc-section-list
All Indian Law & Blogs: https://marriagesolution.in/indian-law/
Full BNSS Section List: https://marriagesolution.in/bnss_section-list
