Introduction of Section 124 BNS
Acid attacks are one of the most brutal forms of violence, leaving victims with lifelong scars, both physical and emotional. To curb this menace, Section 124 of the Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS), 2023 provides strict punishments for causing grievous hurt using acid or corrosive substances. This law not only punishes offenders with long prison terms but also ensures victims receive financial support for medical treatment. By replacing the old IPC provisions, Section 124 brings stronger accountability and a clear framework to fight against such heinous crimes.
The Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS) Section 124 replaces the old Indian Penal Code (IPC) Section 326-B.
What is section 124 of BNS ?
BNS Section 124 of the Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS) deals with the offense of causing grievous hurt by throwing or administering acid or any similar substance. This section also includes the attempt to cause such harm, and provides for strict punishments, including imprisonment for up to life and fines, with a focus on victim compensation.

BNS Act – BNS Section 124
(1) Whoever, by throwing acid or using any corrosive substance, causes grievous hurt to another person—resulting in burns, disfigurement, disability, or permanent/partial damage—shall be punished with imprisonment for not less than 10 years, which may extend to imprisonment for life, and shall also be liable to pay a fine. The fine shall be directed towards the medical treatment and rehabilitation of the victim.
(2) Whoever attempts to throw acid or administer any corrosive substance with the intention of causing grievous hurt, shall be punished with imprisonment for not less than 5 years, which may extend to 7 years, and shall also be liable to pay a fine.
This section deals with the crime of acid attacks—where acid or other corrosive substances are used to cause lasting injuries.
- If someone actually causes grievous hurt (like burns, scars, blindness, or disability), they face 10 years to life imprisonment and a fine.
- If someone only attempts an acid attack (throws but misses, or is caught before causing harm), they still face 5–7 years in prison plus a fine.
- Importantly, the fine collected is meant for the victim’s treatment, acknowledging the heavy financial and emotional burden acid attack survivors face.
Key Elements of Section 124
- Use of Acid or Corrosive Substances → Covers acid, chemicals, or anything corrosive capable of burning or disfiguring.
- Grievous Hurt → Includes permanent scars, burns, disfigurement, disability, or loss of eyesight.
- Attempt Also Punished → Even if the attack fails, the attempt itself is a crime with heavy punishment.
- Minimum Punishment → At least 10 years for causing grievous hurt, and at least 5 years for an attempt.
- Victim Compensation → The fine imposed is specifically to support the victim’s medical care.
- Cognizable & Non-Bailable → Police can arrest without a warrant, and bail is not easily granted.
- Trial in Court of Session → Due to the seriousness of the offense, it is tried in a higher court.
Examples to Understand Section 124
- Example 1 (Grievous Hurt):
A man throws acid on a woman’s face after she rejects his proposal. She suffers permanent facial burns and blindness in one eye.
→ Punishment: Section 124(1) applies → Minimum 10 years to life imprisonment + fine for her medical care. - Example 2 (Attempt):
A person carries a bottle of acid during a fight and tries to throw it, but bystanders stop him before any harm occurs.
→ Punishment: Section 124(2) applies → 5–7 years imprisonment + fine.
Why Section 124 is Important
- It treats acid attacks as one of the gravest crimes.
- It ensures victim compensation, not just punishment for the offender.
- It punishes both the act and the attempt, preventing offenders from escaping with light penalties.
- It protects society by sending a strong deterrent message.
BNS 124 in Simple Points
BNS Section 124(1) – 5 Key Points
- Grievous Hurt by Use of Acid: BNS Section 124(1) addresses cases where a person causes permanent or partial damage, burns, maiming, disfigurement, or disability to another by using acid or similar corrosive substances.
- Intent or Knowledge: The offender must have acted with the intention to cause harm or with the knowledge that their actions would likely result in severe injuries or permanent damage.
- Severe Punishment: The law mandates a minimum imprisonment of 10 years, which can extend to life imprisonment depending on the severity of the harm caused. This strict punishment is designed to deter such violent acts.
- Fine for Victim Compensation: In addition to imprisonment, the offender is liable to pay a fine. The fine is used to meet the medical expenses of the victim, ensuring financial support for the treatment of injuries.
- Non-Bailable and Cognizable: Offenses under BNS Section 124(1) are cognizable, meaning the police can arrest without a warrant, and non-bailable, indicating that the accused may not easily be granted bail due to the seriousness of the offense.
BNS Section 124(2) – 5 Key Points in Detail
- Attempt to Cause Grievous Hurt by Acid: This section applies to cases where a person attempts to throw or administer acid, with the intention of causing grievous hurt, even if no actual harm is done.
- Punishment for Attempt: An attempt to cause harm using acid is also considered a serious crime. The punishment includes imprisonment for a minimum of 5 years, which may extend to 7 years.
- Intent to Harm: The offender must have intended to cause permanent or partial damage, disfigurement, or burns by attempting to use acid or other corrosive substances.
- Fine Imposed: In addition to imprisonment, the offender is also liable to a fine, though the exact amount depends on the severity and nature of the offense.
- Non-Bailable and Cognizable: Similar to Section 124(1), offenses under this subsection are non-bailable and cognizable, reflecting the gravity of even attempting such an act.
Section 124 BNS Overview
BNS Section 124 deals with voluntarily causing grievous hurt by using acid or other corrosive substances. It criminalizes not only the act of causing harm but also the attempt to do so. The section prescribes severe punishments, including imprisonment for up to life, and ensures that fines are imposed to help meet the medical expenses of the victim.
BNS Section 124: 10 Key Points
- Causing Grievous Hurt with Acid:
This section talks about cases where a person uses acid or similar harmful substances to cause serious injuries, such as burns, permanent damage, or disfigurement, to another person. - Intent to Harm:
The person committing the crime must have acted with the intention of causing harm or knowing that their actions would likely result in serious injuries. - Permanent or Partial Damage:
If the acid attack causes permanent or partial damage, such as burns or disabling a part of the body, it is considered grievous hurt, and the punishment is severe. - Punishment for the Offense:
The person who causes such serious harm using acid will be punished with imprisonment for at least 10 years, which can even go up to life imprisonment depending on the severity of the injury. - Fine for Victim’s Medical Expenses:
In addition to the imprisonment, the offender must pay a fine. The fine should be enough to help cover the victim’s medical treatment and recovery. - Non-Bailable Offense:
This crime is non-bailable, meaning the accused cannot easily get bail while awaiting trial due to the seriousness of the offense. - Cognizable Offense:
The police can arrest the accused without a warrant, as this crime is categorized as a cognizable offense. - Attempt to Cause Grievous Hurt with Acid:
If someone tries to throw acid on another person but fails, they can still be punished. Even the attempt to cause harm using acid is treated seriously by the law. - Punishment for Attempting the Crime:
If someone attempts to throw acid but doesn’t succeed, they can be imprisoned for a minimum of 5 years, and the term can extend to 7 years, along with a fine. - Broad Definition of Acid:
The law defines acid broadly. It includes any substance that is corrosive or harmful and can cause burns, scars, or even permanent disability to the victim.
Two Examples of BNS Section 124
- Example 1: A person throws acid at another person during a domestic dispute, resulting in permanent facial burns and disfigurement. Under BNS Section 124(1), the offender is sentenced to a minimum of 10 years in prison and must also pay a fine to cover the victim’s medical treatment.
- Example 2: During a public altercation, an individual attempts to throw acid on someone but is stopped before any injury occurs. Although no physical harm is caused, the offender is still punished under BNS Section 124(2) with a 5-year prison term and fines for the attempt.
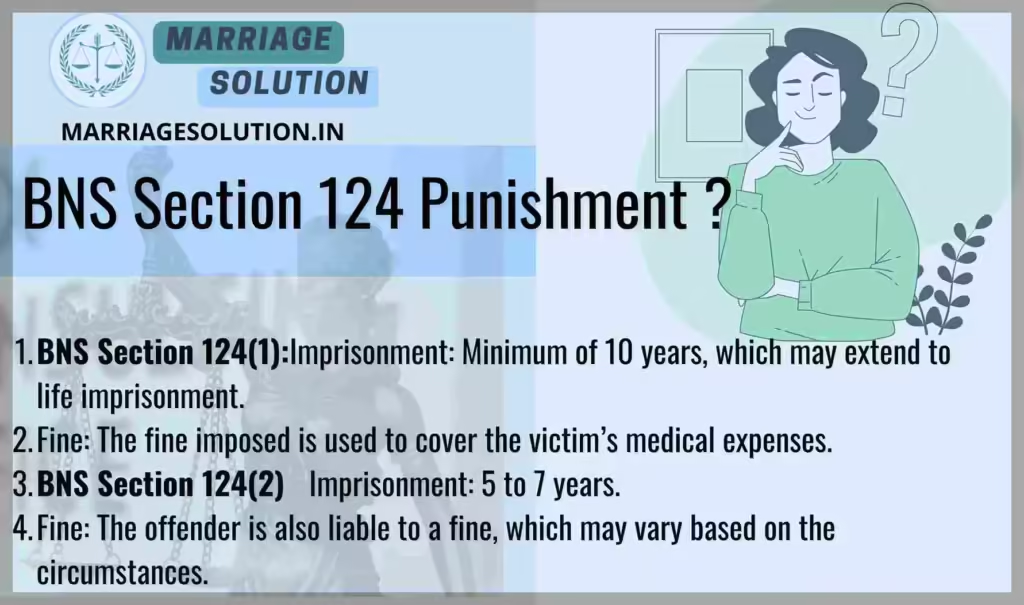
BNS 124 Punishment
- BNS Section 124(1):
- Imprisonment: Minimum of 10 years, which may extend to life imprisonment.
- Fine: The fine imposed is used to cover the victim’s medical expenses.
- BNS Section 124(2):
- Imprisonment: 5 to 7 years.
- Fine: The offender is also liable to a fine, which may vary based on the circumstances.
BNS 124 bailable or not ?
Section 124 offenses are non-bailable, meaning that bail is not easily granted to the accused due to the severity of the crime.
Comparison Table with IPC Section 326A & 326B
| Law Section | Offense | Punishment | Victim Compensation / Fine | Bailable? | Cognizable? | Trial By |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BNS Section 124(1) | Causing grievous hurt by throwing/administering acid or corrosive substances. | Imprisonment not less than 10 years, may extend to life; also liable to fine. | Fine directed towards victim’s medical treatment & rehabilitation. | Non-bailable | Cognizable | Court of Session |
| BNS Section 124(2) | Attempt to throw/administer acid or corrosive substance with intent to cause grievous hurt. | Imprisonment 5–7 years; also liable to fine. | Fine may be used for victim care as ordered by court. | Non-bailable | Cognizable | Court of Session |
| IPC 326A | Causing grievous hurt by acid or corrosive substance (actual attack). | Imprisonment 10 years to life, and fine. | Fine may be imposed (victim relief varies in practice). | Non-bailable | Cognizable | Court of Session |
| IPC 326B | Attempt to throw acid or corrosive substance with intent to cause grievous hurt. | Imprisonment 5–7 years, and fine. | Fine may be imposed (victim relief varies in practice). | Non-bailable | Cognizable | Court of Session |
BNS Section 124 FAQs
What does BNS Section 124 deal with?
It deals with causing grievous hurt by using acid or other harmful substances, leading to severe injuries or deformities.
What is the minimum punishment under this section?
The minimum punishment is 10 years of imprisonment under BNS Section 124(1).
Can someone be punished for attempting to throw acid?
Yes, even attempting to throw or administer acid is punishable with 5 to 7 years of imprisonment.
Is bail available for offenses under BNS Section 124?
No, offenses under this section are non-bailable due to their seriousness.
What is the role of fines in this section?
Fines are imposed to cover the medical expenses of the victim’s treatment.
Conclusion
Section 124 of the BNS stands as one of the strongest legal weapons against acid attacks. By prescribing harsh punishments—including life imprisonment—and ensuring financial support for victims, this law sends a clear message: such heinous crimes will not be tolerated. It not only protects individuals but also reinforces the idea that justice includes both punishment for the offender and care for the victim. In short, BNS Section 124 is a crucial step towards a safer, more just society
Need Legal Support?
If you’re facing court proceedings, marriage-related issues, or any legal matter, our team at Marriage Solution – Lawyer Help is ready to guide you. Just complete our easy online enquiry form, and we’ll connect you with the right legal assistance tailored to your needs.
Finished with BNS 124 ? Continue exploring the next provisions of the Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS), 2023. Each section includes explanations, examples, and plain-language breakdowns for easy understanding.
- 125 BNS :Act endangering life or personal safety of others.
- https://marriagesolution.in/bns_section/125-bns/
- BNS 126 : Wrongful restraint .
- https://marriagesolution.in/bns_section/bns-126/
- 127 BNS : Wrongful confinement .
- https://marriagesolution.in/bns_section/127-bns/
- BNS Section 128 : Force .
- https://marriagesolution.in/bns_section/bns-section-128/
- BNS Section 129 : Criminal force .
- https://marriagesolution.in/bns_section/bns-section-129/
Full IPC Section List: https://marriagesolution.in/ipc-section-list
All Indian Law & Blogs: https://marriagesolution.in/indian-law/
Full BNSS Section List: https://marriagesolution.in/bnss_section-list
