Introduction of BNS Section 275
BNS Section 275 addresses the act of selling food or drink that is harmful or unfit for consumption. It criminalizes the sale, offering, or display of noxious items as consumable goods, especially when the seller is aware of their harmful state. This law aims to safeguard public health by penalizing such offenses.
The Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS) Section 275 replaces the old Indian Penal Code (IPC) Section 273.
- Introduction of BNS Section 275
- What is BNS Section 275 ?
- BNS 275 in Simple Points
- Section 275 BNS Overview
- BNS 275 Punishment
- BNS 275 bailable or not ?
- Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita Section 275
- BNS Section 275 FAQs
- If you need support with court proceedings or any other legal matters, don’t hesitate to reach out for assistance.
What is BNS Section 275 ?
BNS Section 275 defines the offense as selling or offering food or drink that has become harmful or is in an unfit state for consumption, with knowledge or reasonable belief of its harmfulness.

BNS 275 in Simple Points
- Sale of Noxious Food or Drink:
The section covers the sale or display of food or drink that is harmful or unfit for consumption. “Noxious” refers to items that can cause harm, such as spoiled, contaminated, or toxic products. For example, selling spoiled milk or food laced with harmful chemicals constitutes this offense. This provision prioritizes consumer health by ensuring safe and edible goods are sold. - Knowledge or Reasonable Belief:
The law applies to sellers who know or have reason to believe that the food or drink they are selling is harmful. This means negligence or ignorance is not a defense if the seller should have been aware of the item’s condition. For example, selling food past its expiration date knowingly violates this provision. This ensures accountability among sellers. - Scope of the Offense:
The offense includes selling, offering for sale, or even exposing harmful food or drink for sale. Even if the item is not sold but is displayed or offered for purchase, it falls under this section. This broad scope ensures comprehensive protection for consumers from potentially harmful goods. - Punishment for Offenders:
Violators can face imprisonment of up to six months, a fine of ₹5,000, or both. The punishment is designed to act as a deterrent and reflects the seriousness of endangering public health. The dual penalty allows courts to impose a fine or imprisonment based on the gravity of the offense. - Legal Classification:
BNS Section 275 is a non-cognizable, bailable, and non-compoundable offense.- Non-cognizable: Police cannot investigate without the Magistrate’s approval.
- Bailable: The accused has the right to seek bail.
- Non-compoundable: The offense cannot be privately settled; it must be decided in court.
Section 275 BNS Overview
BNS Section 275 addresses the offense of selling, offering, or exposing for sale any food or drink that has become harmful or unfit for human consumption. This section applies when the seller knowingly or has reasonable grounds to believe that the food or drink is harmful, emphasizing the protection of public health and consumer rights.
10 Key Points of BNS Section 275
- Prohibition of Sale of Harmful Food and Drink:
The law prohibits selling or offering harmful or unfit food or drink for human consumption. It ensures food safety by targeting actions that could endanger public health. For example, selling stale, rotten, or chemically contaminated food violates this provision. - Knowledge of Noxiousness:
The offense occurs if the seller knows or has reason to believe that the food or drink is noxious. This ensures accountability by penalizing negligence or willful ignorance. Sellers are expected to inspect and verify the quality of their goods before selling. - Coverage of Sale and Display:
The section not only applies to the actual sale but also to food or drink exposed for sale or offered as edible. Even if the item isn’t sold, displaying it in a harmful state is punishable under this provision. - Consumer Health Protection:
By addressing harmful food and drinks, the section aims to protect consumer health. It ensures that sellers prioritize safety over profit, fostering trust in the food market. - Punishment for Violation:
Violators can face imprisonment of up to six months, a fine of ₹5,000, or both. The punishment reflects the severity of endangering public health and acts as a deterrent. - Legal Classification – Non-Cognizable:
As a non-cognizable offense, the police require approval from a Magistrate to investigate cases under this section. This ensures judicial oversight in food safety cases. - Bailable Offense:
The offense is bailable, meaning the accused has the right to seek bail, ensuring fairness in the legal process. - Non-Compoundable Nature:
The offense is non-compoundable, meaning it cannot be privately settled and must be resolved through a court trial. This emphasizes the public interest in food safety. - Triable by Any Magistrate:
Cases under this section are triable by any Magistrate, ensuring that they can be handled efficiently without requiring higher court intervention. - Deterrent Effect on Vendors:
By criminalizing the sale of harmful food or drink, the law deters vendors from compromising on safety standards. It promotes ethical practices in the food and beverage industry.
Examples of BNS Section 275
- Selling Contaminated Beverages:
A shopkeeper sells soft drinks that are contaminated with harmful chemicals, causing harm to consumers. - Displaying Spoiled Food for Sale:
A vendor displays spoiled fruits for sale despite knowing they are unfit for consumption, violating BNS Section 2275.
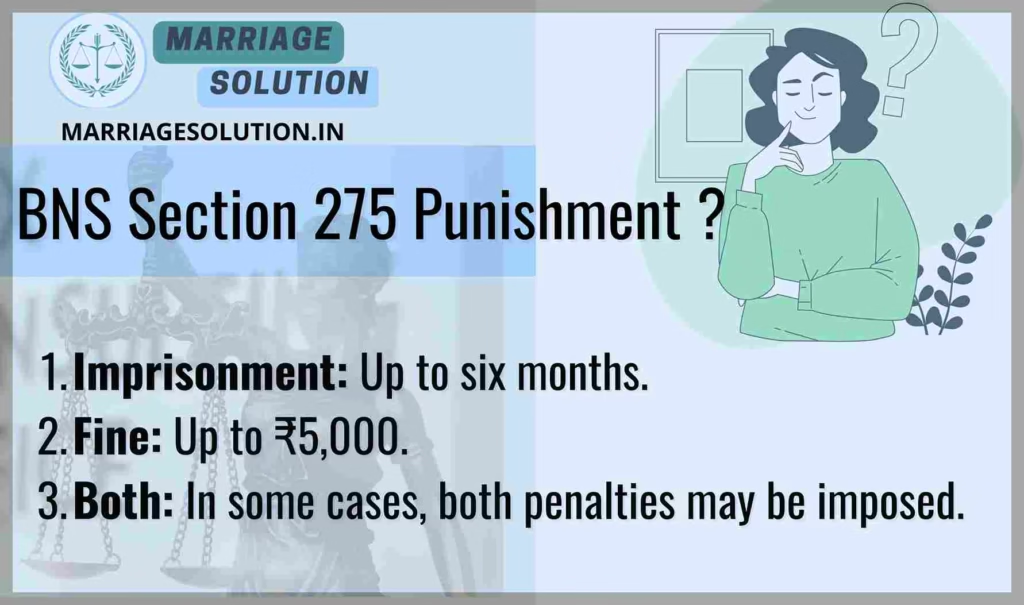
BNS 275 Punishment
- Imprisonment: Up to six months.
- Fine: Up to ₹5,000.
- Both: In some cases, both penalties may be imposed.
BNS 275 bailable or not ?
BNS Section 275 is a bailable offense, allowing the accused to seek bail from the court.
Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita Section 275
| BNS Section | Offense | Punishment | Bailable/Non-Bailable | Cognizable/Non-Cognizable | Trial by |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 275 | Sale of noxious food or drink | Imprisonment up to 6 months, ₹5,000 fine, or both | Bailable | Non-cognizable | Any Magistrate |
BNS Section 275 FAQs
What does BNS Section 275 cover?
It penalizes the sale or display of harmful or unfit food or drink, especially when the seller knows it is unsafe for consumption.
What is the punishment under BNS Section 275?
Punishment includes imprisonment for up to six months, a fine of ₹5,000, or both.
Is BNS Section 275 a bailable offense?
Yes, it is a bailable offense, allowing the accused to secure bail.
What does “noxious” mean in BNS Section 275?
“Noxious” refers to food or drink that is harmful, contaminated, spoiled, or otherwise unfit for consumption.
Who can try cases under BNS Section 275?
Cases under this section are triable by any Magistrate.
If you need support with court proceedings or any other legal matters, don’t hesitate to reach out for assistance.
Court or any other marriage-related issues, our https://marriagesolution.in/lawyer-help-1/ website may prove helpful. By completing our enquiry form and submitting it online, we can provide customized guidance to navigate through the process.
Right to Information RTI act :Your Comprehensive Guide (Part 1)
The Right to Information (RTI) Act : Explore the essence of the Right to Information (RTI) Act through this symbolic image. The image features legal documents, emphasizing the importance of transparency and accountability in governance. The scales of justice represent…
What is Article 371 of Indian Constitution ?
Article 371 of the Indian Constitution grants special provisions to specific states and regions within India, addressing their unique historical, social, and cultural circumstances. These provisions aim to accommodate diverse needs and protect cultural identities within the constitutional framework.
Indian Labour law : Your Comprehensive Guide (Part 1)
The purpose of labour laws is to safeguard employees and guarantee equitable treatment at the workplace, encompassing aspects such as remuneration, security, and perks. These regulations establish a secure ambiance by imposing minimum wage requirements, ensuring factory safety measures are…
GST :Your Comprehensive Guide (Part 1 – Understanding the Basics)
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) is like a big change in how we pay taxes in India. It started on July 1, 2017, and it’s here to simplify things. Before GST, we had many different taxes, and it could…





