Introduction of 201 IPC
201 IPC deals with causing the disappearance of evidence of a crime or providing false information to protect the offender. If someone destroys, hides, or manipulates evidence to shield a criminal, they can be punished under this section. The punishment varies depending on the seriousness of the crime that was concealed.
- Introduction of 201 IPC
- What is IPC Section 201 ?
- IPC 201 in Simple Points
- 1. Destroying or Hiding Evidence is a Crime
- Section 201 IPC Overview
- 10 Key Points of IPC Section 201
- 1. Crime of Destroying or Hiding Evidence
- 2. Giving False Information About a Crime
- 3. Punishment Depends on the Severity of the Crime
- 4. IPC 201 is Applicable Even If the Main Criminal is Not Caught
- 5. Protection for Close Family Members
- 6. Destroying Evidence to Protect Oneself is Also a Crime
- 7. Intent is Necessary for IPC 201
- 8. IPC 201 Can Be Applied With Other IPC Sections
- 9. IPC 201 Covers All Types of Crimes
- 10. The Law Helps Maintain Justice and Prevents Criminals From Escaping
- Example of IPC 201 in Action
- Section 201 IPC case laws
- Case 1: State of Maharashtra v. Damu Gopinath Shinde (2000)
- 201 IPC Bailable or non bailable
- 201 IPC Punishment
- Section 201 IPC in short information
- IPC Section 201 FAQs
- If you need support with court proceedings or any other legal matters, don’t hesitate to reach out for assistance.
What is IPC Section 201 ?
IPC 201 punishes anyone who knowingly hides, destroys, or alters evidence to prevent a criminal from getting caught. It also includes giving false information about a crime to mislead the authorities.

IPC 201 in Simple Points
1. Destroying or Hiding Evidence is a Crime
If a person removes, destroys, or conceals evidence to protect a criminal, they can be punished under IPC 201.
✅ Example: Burning a murder weapon to erase proof.
2. Giving False Information About a Crime is Also Punishable
If someone lies to the police or gives misleading information about a crime, they are guilty under this law.
✅ Example: Saying that a murder happened in another city to divert the police investigation.
3. Punishment Depends on the Seriousness of the Crime
The punishment under IPC 201 is different based on the crime being hidden:
| Crime Being Covered Up | Punishment Under IPC 201 |
|---|---|
| If the crime is punishable by death (e.g., murder) | Up to 7 years imprisonment + fine |
| If the crime is punishable by life imprisonment (e.g., rape, kidnapping) | Up to 3 years imprisonment + fine |
| If the crime is punishable by less than 10 years | 1/4th of the maximum punishment for that crime, or fine, or both |
✅ Example: A person hides a dead body after a murder → Punishment up to 7 years in jail.
4. IPC 201 Applies Even If the Main Criminal is Not Caught
Even if the real criminal is never convicted, the person who destroyed evidence can still be punished under IPC 201.
✅ Example: A person deletes CCTV footage of a robbery, even if the robber is never found, they can still be jailed.
5. Immediate Family Members May Get Some Protection
If a close family member (like a parent or spouse) helps a criminal, they may be given some legal protection. However, this does not apply in serious cases like murder, terrorism, or rape.
✅ Example: A mother hides her son after he committed a minor theft → She may not be punished.
✅ Example: A wife destroys a murder weapon used by her husband → She can be punished under IPC 201.
Section 201 IPC Overview
IPC Section 201 is a strict law that punishes those who destroy or hide evidence of a crime. The punishment varies depending on the seriousness of the crime being concealed. This law is crucial in maintaining the integrity of the justice system by ensuring that evidence is not manipulated.
10 Key Points of IPC Section 201
1. Crime of Destroying or Hiding Evidence
- If a person removes, destroys, or conceals evidence of a crime, they are guilty under IPC 201.
- The crime must be committed with the intention of helping the offender escape punishment.
✅ Example: A person burns a blood-stained knife used in a murder to protect the killer.
2. Giving False Information About a Crime
- A person is guilty under IPC 201 if they provide false information to the police or court about a crime.
- This includes giving false statements, fake witness testimonies, or misleading reports.
✅ Example: A person tells the police that the murder happened in another city to divert the investigation.
3. Punishment Depends on the Severity of the Crime
IPC 201 provides different punishments based on the original crime that was covered up:
| Crime Being Covered Up | Punishment Under IPC 201 |
|---|---|
| Crime punishable by death (e.g., murder) | Up to 7 years imprisonment + fine |
| Crime punishable by life imprisonment (e.g., kidnapping, rape) | Up to 3 years imprisonment + fine |
| Crime punishable with imprisonment under 10 years (e.g., theft, cheating) | 1/4th of the maximum punishment for that crime, or fine, or both |
✅ Example: If a person hides a dead body in a murder case, they can get 7 years in jail.
4. IPC 201 is Applicable Even If the Main Criminal is Not Caught
- The offender can be punished under IPC 201 even if the main criminal is never convicted.
- The court only needs proof that the evidence was tampered with intentionally.
✅ Example: A person destroys CCTV footage of a robbery, even if the robber is never arrested, can be punished under IPC 201.
5. Protection for Close Family Members
- Immediate family members (parents, spouses, children) who help cover up a crime are usually not punished under IPC 201.
- However, this exception does not apply in serious cases like murder, terrorism, or rape.
✅ Example: A mother hides her son after he steals money → She may not be punished under IPC 201.
✅ Example: A wife destroys evidence of her husband’s murder case → She can be punished under IPC 201.
6. Destroying Evidence to Protect Oneself is Also a Crime
- If a person destroys evidence to save themselves, they can still be charged under IPC 201.
✅ Example: A driver hits a pedestrian and then burns his car to remove evidence → He is guilty under IPC 201.
7. Intent is Necessary for IPC 201
- A person can be convicted only if they knowingly destroyed evidence.
- If the destruction was accidental or without intention, IPC 201 does not apply.
✅ Example: A janitor accidentally throws away a murder weapon → Not guilty.
✅ Example: A person deliberately burns a suicide note to protect the accused → Guilty under IPC 201.
8. IPC 201 Can Be Applied With Other IPC Sections
- IPC 201 is usually added with other IPC sections, depending on the case.
- Common sections used with IPC 201:
- IPC 302 (Murder)
- IPC 376 (Rape)
- IPC 409 (Criminal Breach of Trust by a Public Servant)
✅ Example: If a person commits a crime and then removes fingerprints, they can be charged under both the crime section and IPC 201.
9. IPC 201 Covers All Types of Crimes
- IPC 201 applies to all offenses, whether major or minor.
- However, the punishment depends on the seriousness of the original crime.
✅ Example: Hiding evidence in a corruption case is a lesser offense than hiding evidence in a murder case.
10. The Law Helps Maintain Justice and Prevents Criminals From Escaping
- IPC 201 is important because it prevents criminals from escaping punishment by destroying evidence.
- The law ensures that no one can manipulate justice by misleading authorities.
✅ Example: A person removes a dead body from a crime scene → IPC 201 ensures they get punished for helping the real offender.
Example of IPC 201 in Action
A knows that B has murdered Z. A helps B hide the dead body to prevent B from getting caught.
🔹 What crime has A committed? → A has violated IPC 201.
🔹 What is the punishment? → 7 years imprisonment + fine (since the original crime was murder).
Section 201 IPC case laws
Case 1: State of Maharashtra v. Damu Gopinath Shinde (2000)
Facts:
- The accused helped dispose of a dead body to hide a murder.
- The police found evidence linking the accused to the crime.
Judgment: - The accused was convicted under IPC 201 and sentenced to 7 years of imprisonment for destroying evidence in a murder case.
Case 2: Kalawati v. State of Himachal Pradesh (1953)
Facts:
- A woman wiped blood stains from a murder scene to protect her husband.
- The police found forensic proof of her involvement in hiding the crime.
Judgment: - The court held that she actively helped in hiding evidence, making her guilty under IPC 201.
- She was sentenced to 3 years of imprisonment.
Case 3: Satpal v. State of Haryana (2018)
Facts:
- The accused deleted CCTV footage of a robbery at a shop to protect the criminals.
- The police later recovered the footage from backup files.
Judgment: - The court found that destroying digital evidence is also punishable under IPC 201.
- The accused received 2 years of imprisonment and a fine.
Case 4: Raghunath v. State of Uttar Pradesh (1981)
Facts:
- A person misled the police by giving false statements about a murder.
- His false testimony delayed the investigation.
Judgment: - The Supreme Court ruled that providing false information to obstruct justice is a crime under IPC 201.
- The accused was sentenced to 5 years of imprisonment.
Case 5: State v. Suresh Kumar (2021)Facts:
- The accused burned clothes with blood stains to remove evidence of an assault.
- The forensic team detected traces of blood on ashes.
Judgment: - The court convicted him under IPC 201, sentencing him to 3 years of imprisonment.
201 IPC Bailable or non bailable
🔹 Bailable or Non-Bailable? – IPC 201 can be bailable or non-bailable, depending on the seriousness of the crime concealed.
🔹 If the hidden offense is punishable by death or life imprisonment, IPC 201 becomes non-bailable.
🔹 If the hidden offense carries imprisonment below ten years, IPC 201 is generally bailable.
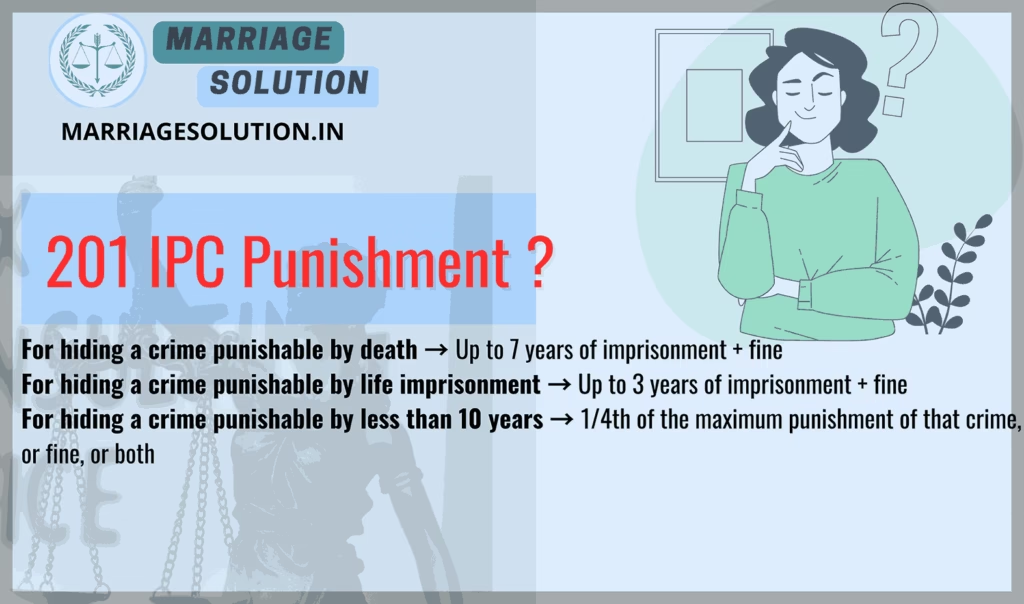
201 IPC Punishment
1️⃣ For hiding a crime punishable by death → Up to 7 years of imprisonment + fine
2️⃣ For hiding a crime punishable by life imprisonment → Up to 3 years of imprisonment + fine
3️⃣ For hiding a crime punishable by less than 10 years → 1/4th of the maximum punishment of that crime, or fine, or both
Section 201 IPC in short information
| IPC Section | Offense | Punishment | Bailable/Non-Bailable | Cognizable/Non-Cognizable | Trial By |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 201 IPC | Hiding evidence or giving false information to shield a criminal | Up to 7 years imprisonment + fine (varies with crime) | Bailable for minor crimes, Non-Bailable for serious crimes | Cognizable if related to serious crimes | Magistrate |
IPC Section 201 FAQs
What is IPC 201?
IPC 201 punishes anyone who hides evidence of a crime or provides false information to protect a criminal from punishment.
What is the punishment under IPC 201?
The punishment depends on the crime being hidden:
If the crime carries imprisonment of less than 10 years → 1/4th of the maximum punishment of that crime or fine, or both
If the concealed crime is punishable by death → Up to 7 years of imprisonment + fine
If punishable by life imprisonment → Up to 3 years of imprisonment + fine
Is IPC 201 a bailable offense?
If the hidden crime is serious (punishable by death or life imprisonment), IPC 201 is non-bailable.
For lesser crimes (punishable by less than 10 years), IPC 201 is bailable.
Is IPC 201 a cognizable or non-cognizable offense?
For minor offenses, IPC 201 is non-cognizable.
If the crime concealed is serious (death penalty/life imprisonment), IPC 201 is cognizable.
Can a person be charged under IPC 201 if they unknowingly destroyed evidence?
No. To be guilty under IPC 201, the person must have knowingly or intentionally hidden evidence or provided false information to protect the offender. If the act was done unknowingly, IPC 201 does not apply.
If you need support with court proceedings or any other legal matters, don’t hesitate to reach out for assistance.
Court or any other marriage-related issues, our https://marriagesolution.in/lawyer-help-1/ website may prove helpful. By completing our enquiry form and submitting it online, we can provide customized guidance to navigate through the process.
Right to Information RTI act :Your Comprehensive Guide (Part 1)
The Right to Information (RTI) Act : Explore the essence of the Right to Information (RTI) Act through this symbolic image. The image features legal documents, emphasizing the importance of transparency and accountability in governance. The scales of justice represent…
What is Article 371 of Indian Constitution ?
Article 371 of the Indian Constitution grants special provisions to specific states and regions within India, addressing their unique historical, social, and cultural circumstances. These provisions aim to accommodate diverse needs and protect cultural identities within the constitutional framework.
Indian Labour law : Your Comprehensive Guide (Part 1)
The purpose of labour laws is to safeguard employees and guarantee equitable treatment at the workplace, encompassing aspects such as remuneration, security, and perks. These regulations establish a secure ambiance by imposing minimum wage requirements, ensuring factory safety measures are…
GST :Your Comprehensive Guide (Part 1 – Understanding the Basics)
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) is like a big change in how we pay taxes in India. It started on July 1, 2017, and it’s here to simplify things. Before GST, we had many different taxes, and it could…





