Introduction of Section 332 IPC
IPC Section 332 deals with cases where someone attacks or hurts a public servant while they are doing their job. This law aims to protect public servants like police officers, doctors, or government workers from being harmed while carrying out their duties.

1.Definition of IPC 332 ?
IPC Section 332 is a law in India that punishes those who harm public servants while they’re on duty. It can lead to imprisonment for up to three years and a fine. This law is crucial for protecting public servants and maintaining law and order.
2.IPC Section 332
1. Deliberate Harm
- This means the person causing harm to the public servant does it on purpose. It’s not an accident – they intend to hurt them.
- For example, if someone hits a police officer during a protest because they want to stop them from arresting someone, that’s deliberate harm under IPC Section 332.
2.Types of Harm:
- The injury could be as small as a bruise or as serious as a broken bone or internal damage.
- Actions like hitting, punching, kicking, or any other physical attack that causes harm fall under this category.
3.Intent to Stop
- The person hurting the public servant wants to prevent them from doing their job. They use violence to scare or intimidate them, hoping they’ll back off from their duties.
- This could involve threatening a government official to stop them from enforcing the law or attacking a doctor to prevent them from treating a patient.
4.Who’s Covered
- IPC Section 332 applies to various public service roles, including police officers, government officials, healthcare workers, firefighters, and others working for the public good.
- Anyone who tries to stop them from doing their job by hurting them could be breaking the law under IPC Section 332.
5.Severity of Punishment
- Imprisonment for up to three years and a fine are prescribed.
- Reflects the seriousness of obstructing or intimidating public servants under the law.
6.Protective Measures
- IPC Section 332 safeguards public servants’ safety.
- Ensures law and order and maintains public trust in government institutions.
7.Exceptions and Justifications
- Certain exceptions exist, like self-defense or lawful duties.
- Prohibits deliberate harm to public servants except in specific circumstances.
8.Societal Implications
- IPC Section 332 crucial for societal harmony and public service integrity.
- Reinforces respect for authority and underscores the consequences of obstructing justice.
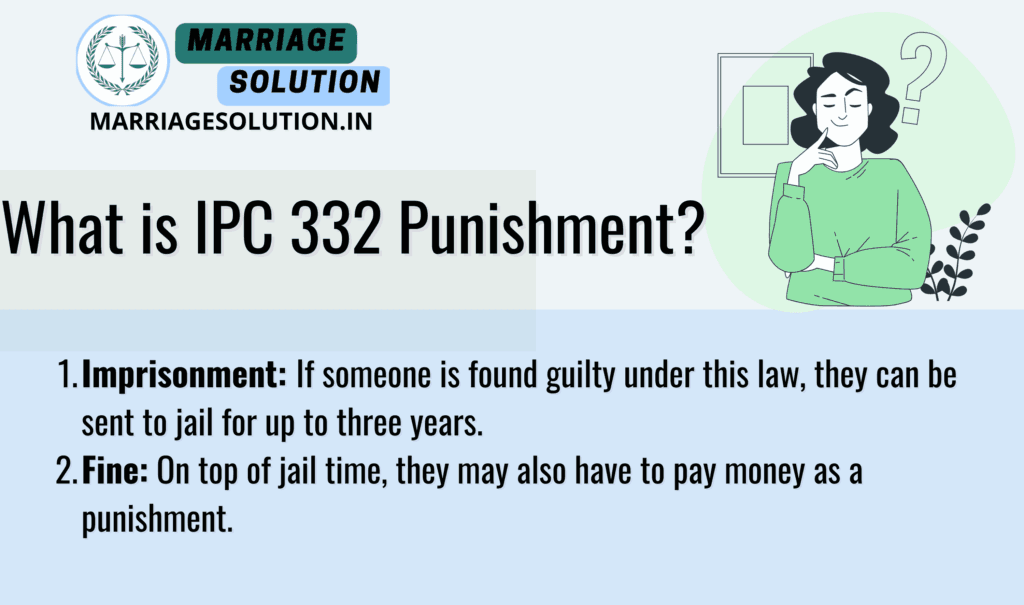
IPC 332 Punishment
- Harming Public Servants: This law deals with situations where someone hurts a public servant on purpose, trying to stop them from doing their job.
- Imprisonment: If someone is found guilty under this law, they can be sent to jail for up to three years.
- Fine: On top of jail time, they may also have to pay money as a punishment.
- Why Punishment?: This punishment is to stop people from hurting or getting in the way of public servants while they work. It’s important for keeping our government running smoothly and making sure everyone follows the rules.
- Where It Comes From: This law is part of a bigger set of rules called the Indian Penal Code, which lays out what’s right and wrong in India and what happens if someone breaks the law.
332 IPC bailable or not ?
- Non-Bailable Offense:
- IPC Section 332 categorizes as a non-bailable offense.
- Accused individuals cannot obtain bail automatically.
- Court Discretion:
- Accused persons charged under IPC Section 332 cannot secure bail by right.
- They must petition the court for bail, and it’s the court’s decision whether to grant it.
- Factors Considered:
- Various factors influence the court’s decision on bail.
- These include the gravity of the offense, evidence strength, likelihood of the accused absconding, and potential tampering with evidence.
- Judicial Process:
- Those accused under IPC Section 332 may remain in custody until their bail application is reviewed and decided by the court.
- The court examines all relevant aspects before making a ruling on bail.
- Legal Representation:
- Accused individuals have the right to legal representation.
- Legal counsel assists in effectively presenting the case for bail before the court.
IPC Section 332 FAQs
What is IPC Section 332?
IPC Section 332 is a part of the law that deals with hurting public servants to stop them from doing their job.
What counts as breaking IPC Section 332?
It’s when someone hurts a public servant on purpose to stop them from doing their duty.
What’s the punishment for breaking IPC Section 332?
The punishment can be up to three years in jail and sometimes a fine too.
Can someone get bail if accused under IPC Section 332?
No, it’s not easy. They have to ask the court for bail, and the court decides if they can get it or not.
If you require assistance with court or any other Cases.
court or any other marriage-related issues, our https://marriagesolution.in/lawyer-help-1/ website may prove helpful. By completing our enquiry form and submitting it online, we can provide customized guidance to navigate through the process effectively. Don’t hesitate to contact us for personalized solutions; we are here to assist you whenever necessary!
Official website of the Maharashtra government’s police department for help and support.
https://www.mahapolice.gov.in/ https://www.mahapolice.gov.in/ visit the official website of the Maharashtra government for any requirements or inquiries.
- AFSPA Act
 AFSPA act mean Armed Forces Special Powers Act (AFSPA) grants special powers to the Indian Armed Forces in areas classified as “disturbed” due to significant insurgency or internal disturbances.
AFSPA act mean Armed Forces Special Powers Act (AFSPA) grants special powers to the Indian Armed Forces in areas classified as “disturbed” due to significant insurgency or internal disturbances. - Right to Information RTI act :Your Comprehensive Guide (Part 1)
 The Right to Information (RTI) Act : Explore the essence of the Right to Information (RTI) Act through this symbolic image. The image features legal documents, emphasizing the importance of transparency and accountability in governance. The scales of justice represent the balance achieved through the citizens’ right to access information.
The Right to Information (RTI) Act : Explore the essence of the Right to Information (RTI) Act through this symbolic image. The image features legal documents, emphasizing the importance of transparency and accountability in governance. The scales of justice represent the balance achieved through the citizens’ right to access information. - What is Article 371 of Indian Constitution ?
 Article 371 of the Indian Constitution grants special provisions to specific states and regions within India, addressing their unique historical, social, and cultural circumstances. These provisions aim to accommodate diverse needs and protect cultural identities within the constitutional framework.
Article 371 of the Indian Constitution grants special provisions to specific states and regions within India, addressing their unique historical, social, and cultural circumstances. These provisions aim to accommodate diverse needs and protect cultural identities within the constitutional framework. - Indian Labour law : Your Comprehensive Guide (Part 1)
 The purpose of labour laws is to safeguard employees and guarantee equitable treatment at the workplace, encompassing aspects such as remuneration, security, and perks. These regulations establish a secure ambiance by imposing minimum wage requirements, ensuring factory safety measures are implemented effectively while granting rights like maternal leave entitlements. Abiding by these principles promulgates an impartial work culture encapsulating upright conduct; thereby cultivating conducive surroundings for progressive development.
The purpose of labour laws is to safeguard employees and guarantee equitable treatment at the workplace, encompassing aspects such as remuneration, security, and perks. These regulations establish a secure ambiance by imposing minimum wage requirements, ensuring factory safety measures are implemented effectively while granting rights like maternal leave entitlements. Abiding by these principles promulgates an impartial work culture encapsulating upright conduct; thereby cultivating conducive surroundings for progressive development. - GST :Your Comprehensive Guide (Part 1 – Understanding the Basics)
 The Goods and Services Tax (GST) is like a big change in how we pay taxes in India. It started on July 1, 2017, and it’s here to simplify things. Before GST, we had many different taxes, and it could get confusing. Now, with GST, it’s like combining all those taxes into one. The idea is to make taxes more straightforward, clear, and fair for everyone. It applies to almost everything we buy or sell, and it’s helping India’s businesses and economy work better together. So, GST is not just a tax change; it’s a step towards making things simpler and better for all of us.
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) is like a big change in how we pay taxes in India. It started on July 1, 2017, and it’s here to simplify things. Before GST, we had many different taxes, and it could get confusing. Now, with GST, it’s like combining all those taxes into one. The idea is to make taxes more straightforward, clear, and fair for everyone. It applies to almost everything we buy or sell, and it’s helping India’s businesses and economy work better together. So, GST is not just a tax change; it’s a step towards making things simpler and better for all of us.





