Introduction
IPC Section 356 protects you from theft with force in public. It applies when someone uses threats or shoves you to steal your belongings.
- Introduction
- What is IPC 356 ?
- Definition of IPC 356
- section 356 IPC explanation
- Section 356 IPC Punishment
- 356 IPC bailable or not
- IPC 356 FAQs
- If you need support with court proceedings or any other legal matters, don’t hesitate to reach out for assistance.
- Official website of the Maharashtra government’s police department for help and support.
What is IPC 356 ?
Worried about getting robbed? IPC Section 356 has your back! It protects you from theft in public when someone uses shoves or threats, like a snatching or a pickpocket trying to escape.

Definition of IPC 356
IPC Section 356 protects individuals from theft committed with force, such as shoving or threats, in public spaces. It focuses on the intent to steal rather than just the physical act, aiming to safeguard against such incidents.
section 356 IPC explanation
1. When Does It Apply?
This section kicks in when someone uses physical force or threats to steal your belongings in public. This could be:
- A snatching of your purse or phone.
- A pickpocket trying to steal from you and pushing you away when confronted.
2. Intent is Crucial
Just a shove or argument wouldn’t qualify. For it to be a crime under Section 356, the person must have the intention to steal from you using force or threats.
3. Examples (not exhaustive):
- Scenario 1: Someone grabs your belongings in public and threatens you with harm if you make a scene. This is a clear case of using force to steal.
- Scenario 2: While on public transportation, someone attempts to take your phone without your permission and pushes you away when you try to stop them. This situation falls under Section 356.
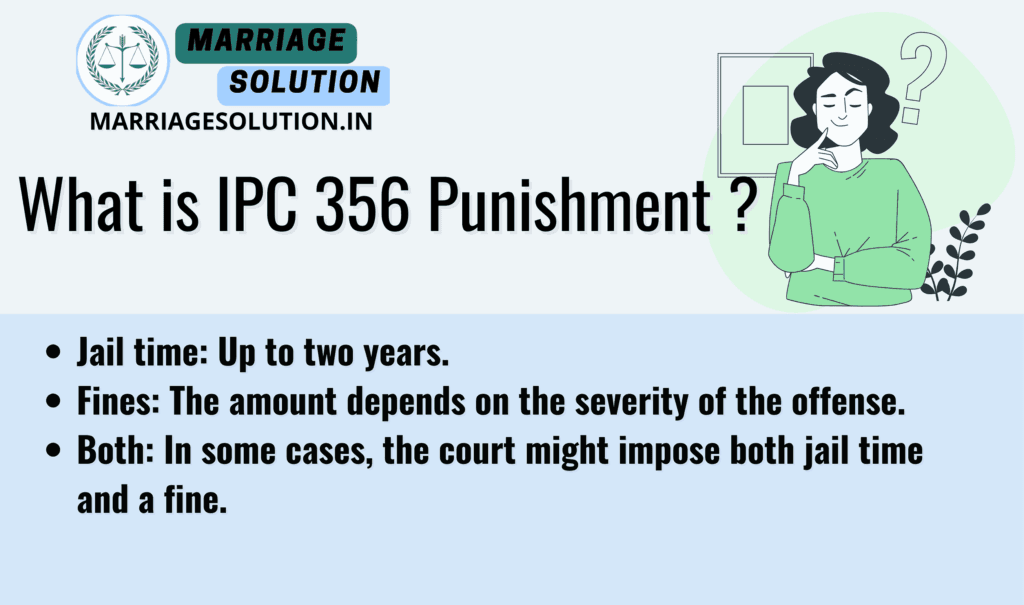
4. Punishment for Offenders:
If someone is found guilty of violating Section 356, they could face:
- Jail time: Up to two years.
- Fines: The amount depends on the severity of the offense.
- Both: In some cases, the court might impose both jail time and a fine.
5. Getting Released Before Trial (Bail):
Offenses under Section 356 are generally considered bailable. However, the court has the final say. They consider factors like:
- Severity of the Offense: A minor snatching might be treated differently than a violent robbery.
- Accused’s Past: If the person has a history of crime, bail might be less likely.
Section 356 IPC Punishment
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Offence | IPC Section 356 covers assault or criminal force in an attempt to commit theft. |
| Definition | It involves using force or assault to facilitate theft, such as snatching belongings or pickpocketing. |
| Punishment | Offenders can face imprisonment for up to three years or a fine, or both, as determined by the court. |
| bailable | Offences under IPC Section 356 are generally bailable, but bail decisions depend on the court’s discretion and the specific circumstances of the case. |
356 IPC bailable or not
IPC Section 356 offenses are usually bailable, but the decision to grant bail depends on the details of the case and the court’s discretion. Factors such as the seriousness of the offense and the likelihood of the accused fleeing or interfering with the case influence the bail decision.
IPC 356 FAQs
What does Section 356 protect me from?
This law protects you from getting robbed in public when someone uses shoves or threats to steal your belongings. Think of someone snatching your bag or a pickpocket pushing you to take your phone.
What makes an action an offence under Section 356?
An offence under Section 356 occurs when force is intentionally used to aid theft. For example, snatching someone’s bag or wallet by pushing or threatening them.
Can someone get bail under IPC 356 Section?
Maybe. It depends on the situation. The court considers things like how serious the crime was and if the person has done something like this
Can offenders get bail?
Offences under Section 356 are usually bailable, but it’s up to the court to decide based on factors like the seriousness of the offence and the safety of the victim.
If you need support with court proceedings or any other legal matters, don’t hesitate to reach out for assistance.
Court or any other marriage-related issues, our https://marriagesolution.in/lawyer-help-1/ website may prove helpful. By completing our enquiry form and submitting it online, we can provide customized guidance to navigate through the process effectively. Don’t hesitate to contact us for personalized solutions; we are here to assist you whenever necessary!
- AFSPA Act
 AFSPA act mean Armed Forces Special Powers Act (AFSPA) grants special powers to the Indian Armed Forces in areas classified as “disturbed” due to significant insurgency or internal disturbances.
AFSPA act mean Armed Forces Special Powers Act (AFSPA) grants special powers to the Indian Armed Forces in areas classified as “disturbed” due to significant insurgency or internal disturbances. - Right to Information RTI act :Your Comprehensive Guide (Part 1)
 The Right to Information (RTI) Act : Explore the essence of the Right to Information (RTI) Act through this symbolic image. The image features legal documents, emphasizing the importance of transparency and accountability in governance. The scales of justice represent the balance achieved through the citizens’ right to access information.
The Right to Information (RTI) Act : Explore the essence of the Right to Information (RTI) Act through this symbolic image. The image features legal documents, emphasizing the importance of transparency and accountability in governance. The scales of justice represent the balance achieved through the citizens’ right to access information. - What is Article 371 of Indian Constitution ?
 Article 371 of the Indian Constitution grants special provisions to specific states and regions within India, addressing their unique historical, social, and cultural circumstances. These provisions aim to accommodate diverse needs and protect cultural identities within the constitutional framework.
Article 371 of the Indian Constitution grants special provisions to specific states and regions within India, addressing their unique historical, social, and cultural circumstances. These provisions aim to accommodate diverse needs and protect cultural identities within the constitutional framework. - Indian Labour law : Your Comprehensive Guide (Part 1)
 The purpose of labour laws is to safeguard employees and guarantee equitable treatment at the workplace, encompassing aspects such as remuneration, security, and perks. These regulations establish a secure ambiance by imposing minimum wage requirements, ensuring factory safety measures are implemented effectively while granting rights like maternal leave entitlements. Abiding by these principles promulgates an impartial work culture encapsulating upright conduct; thereby cultivating conducive surroundings for progressive development.
The purpose of labour laws is to safeguard employees and guarantee equitable treatment at the workplace, encompassing aspects such as remuneration, security, and perks. These regulations establish a secure ambiance by imposing minimum wage requirements, ensuring factory safety measures are implemented effectively while granting rights like maternal leave entitlements. Abiding by these principles promulgates an impartial work culture encapsulating upright conduct; thereby cultivating conducive surroundings for progressive development. - GST :Your Comprehensive Guide (Part 1 – Understanding the Basics)
 The Goods and Services Tax (GST) is like a big change in how we pay taxes in India. It started on July 1, 2017, and it’s here to simplify things. Before GST, we had many different taxes, and it could get confusing. Now, with GST, it’s like combining all those taxes into one. The idea is to make taxes more straightforward, clear, and fair for everyone. It applies to almost everything we buy or sell, and it’s helping India’s businesses and economy work better together. So, GST is not just a tax change; it’s a step towards making things simpler and better for all of us.
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) is like a big change in how we pay taxes in India. It started on July 1, 2017, and it’s here to simplify things. Before GST, we had many different taxes, and it could get confusing. Now, with GST, it’s like combining all those taxes into one. The idea is to make taxes more straightforward, clear, and fair for everyone. It applies to almost everything we buy or sell, and it’s helping India’s businesses and economy work better together. So, GST is not just a tax change; it’s a step towards making things simpler and better for all of us.
Official website of the Maharashtra government’s police department for help and support.
https://www.mahapolice.gov.in/ https://www.mahapolice.gov.in/ visit the official website of the Maharashtra government for any requirements or inquiries.





